1. 使用工具和学习路径
中文官网地址: https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/
使用工具 Hbuilder X
2. 基础知识
- 常用指令
- v-bind
- v-mode
- v-for
<dev id=appx> <ul> <li v-for="item in items"> {{ itme.title }} </li> </ul> </dev> <script> var vm = new Vue({ el:"#appx", data:{ items: [ {"title": "张三"}, {"title": "李四"}, {"title": "王五"}, ] }) </script>
- v-if
- 单项数据绑定和双向数据绑定 xxxxx
Vue()子类的使用
对象实例以及对象实例的调用
<script> var vm = new Vue({ el:"#appxxx", data:{ title:"我vuejs学习", url:"http://www.baidu.com" } }) // vm.$el 就相当于 document.getElementById("appxxx") //样式设置为红色 vm.$.el.style.color = "red"; </script>
vue.js 文件引用
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <script src="vue.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app"> {{ message }} {{name}} </div> <script type="text/javascript"> var app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { message: 'Hello Vue!', name : "Vue" } }); </script> </body> </html>
- 数据和方法(用实例的方法 $watch 观察变量值改变前后情况 )
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <script src="vue.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app"> {{a}} </div> <script type="text/javascript"> var data = { a : 1 }; var vm = new Vue({ el : "#app", data : data }); vm.$watch('a', function(newVal, oldVal){ console.log(newVal, oldVal); }) vm.$data.a = "test...." </script> </body> </html>
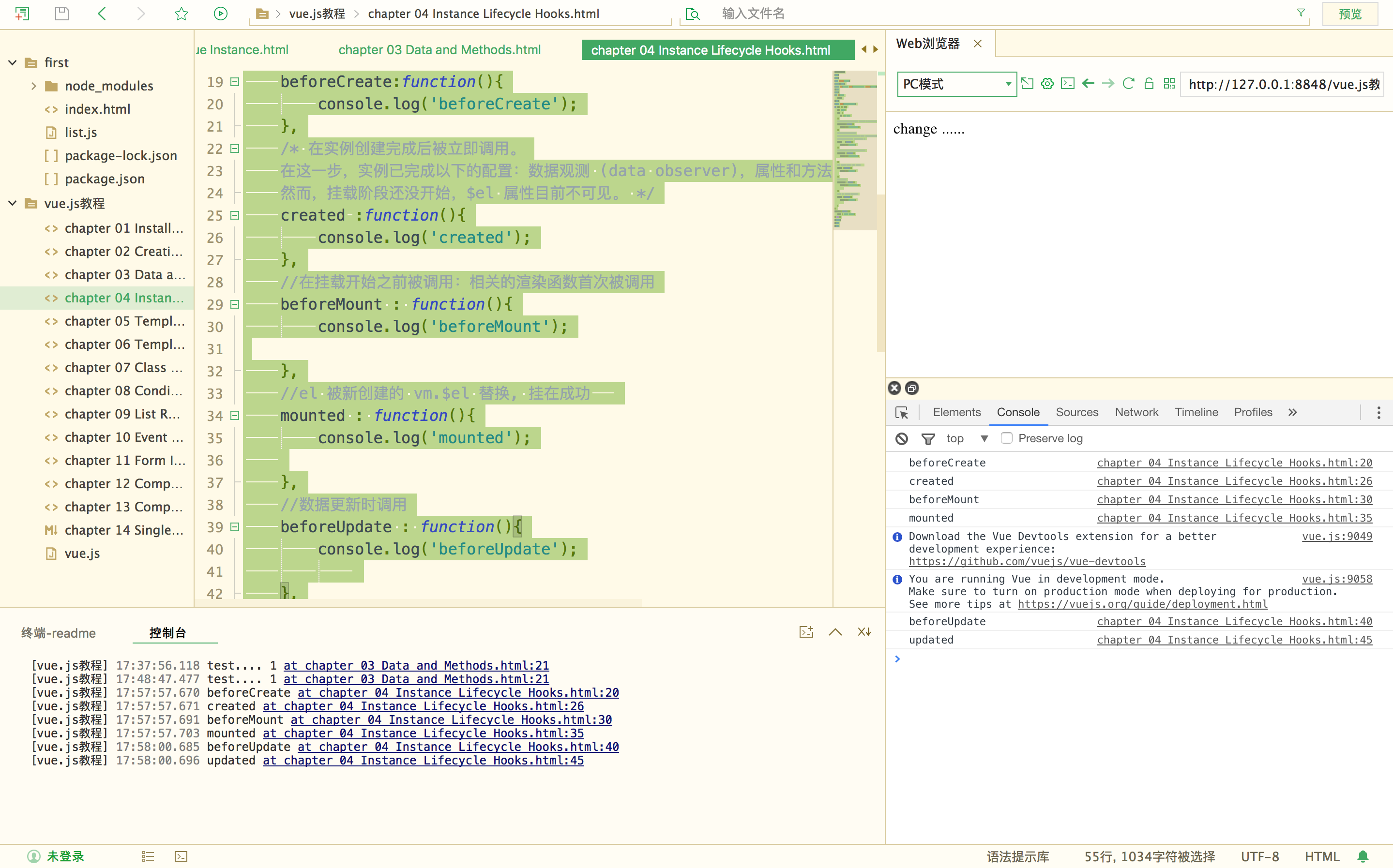
实例生命周期
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <script src="vue.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app"> {{msg}} </div> <script type="text/javascript"> var vm = new Vue({ el : "#app", data : { msg : "hi vue", }, //在实例初始化之后,数据观测 (data observer) 和 event/watcher 事件配置之前被调用。 beforeCreate:function(){ console.log('beforeCreate'); }, /* 在实例创建完成后被立即调用。 在这一步,实例已完成以下的配置:数据观测 (data observer),属性和方法的运算,watch/event 事件回调。 然而,挂载阶段还没开始,$el 属性目前不可见。 */ created :function(){ console.log('created'); }, //在挂载开始之前被调用:相关的渲染函数首次被调用 beforeMount : function(){ console.log('beforeMount'); }, //el 被新创建的 vm.$el 替换, 挂在成功 mounted : function(){ console.log('mounted'); }, //数据更新时调用 beforeUpdate : function(){ console.log('beforeUpdate'); }, //组件 DOM 已经更新, 组件更新完毕 updated : function(){ console.log('updated'); } }); setTimeout(function(){ vm.msg = "change ......"; }, 3000); </script> </body> </html>
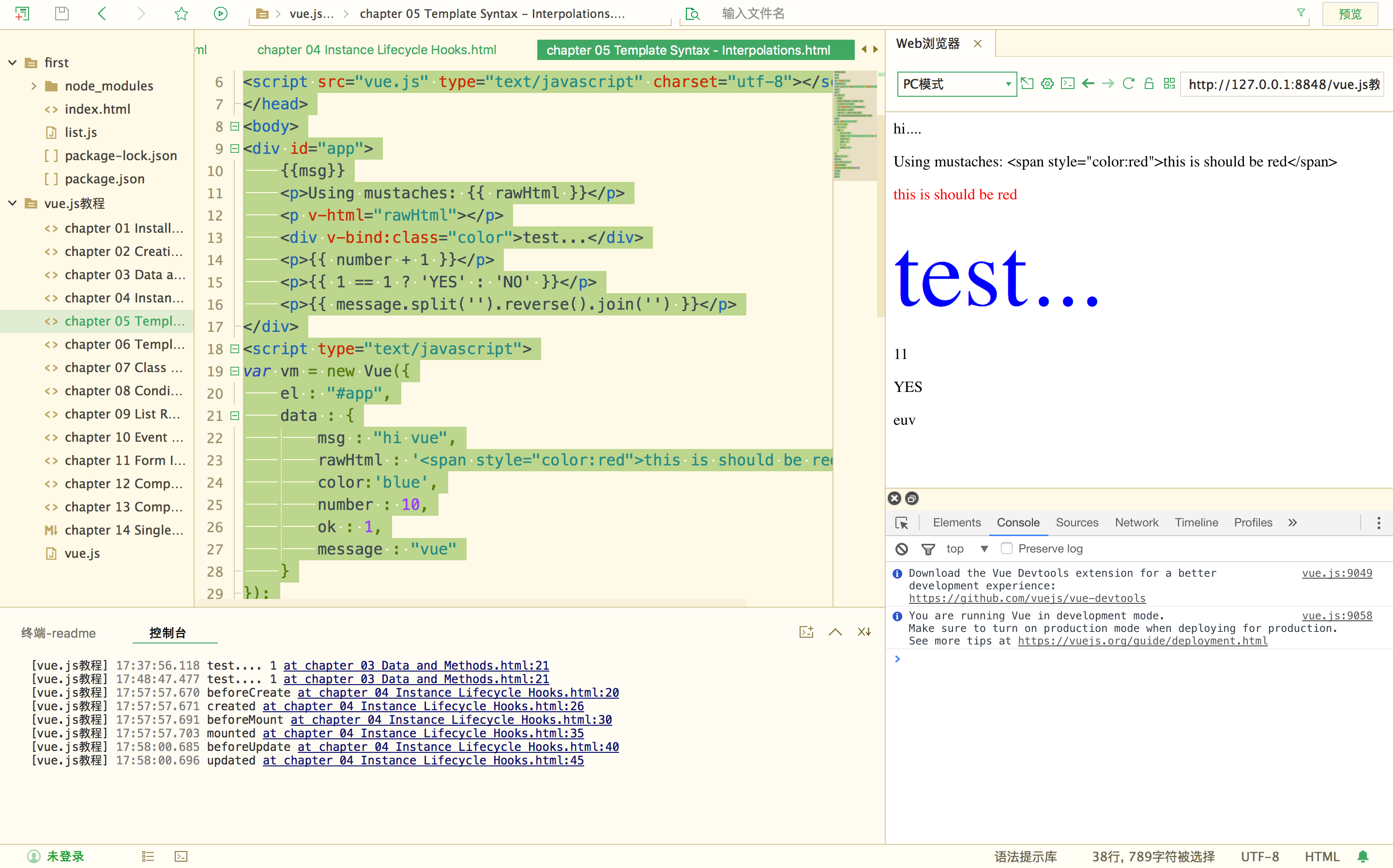
模板语法-插值
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <script src="vue.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app"> {{msg}} <p>Using mustaches: {{ rawHtml }}</p> <p v-html="rawHtml"></p> <div v-bind:class="color">test...</div> <p>{{ number + 1 }}</p> <p>{{ 1 == 1 ? 'YES' : 'NO' }}</p> <p>{{ message.split('').reverse().join('') }}</p> </div> <script type="text/javascript"> var vm = new Vue({ el : "#app", data : { msg : "hi vue", rawHtml : '<span style="color:red">this is should be red</span>', color:'blue', number : 10, ok : 1, message : "vue" } }); vm.msg = "hi...."; </script> <style type="text/css"> .red{color:red;} .blue{color:blue; font-size:100px;} </style> </body> </html>
模板属性-指令
v-bind 绑定的是属性, v-on 绑定的是事件
<! -- 动态参数 -->
<a v-bind:[attributeName]="url"> ... </a>
<a v-on:[eventName]="doSomething"> ... </a>
<-! Vue 实例有一个 data--></-!>
data : {
attributeName: "href",
eventName: "click"
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<script src="vue.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p v-if="seen">现在你看到我了</p>
<a v-bind:href="url">...</a>
<div @click="click1">
<div @click.stop="click2">
click me
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vm = new Vue({
el : "#app",
data : {
seen : false,
url : "https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/syntax.html#%E6%8C%87%E4%BB%A4"
},
methods:{
click1 : function () {
console.log('click1......');
},
click2 : function () {
console.log('click2......');
}
}
});
</script>
<style type="text/css">
</style>
</body>
</html>
- 计算属性和侦听器
<div id="example">
<p>Original message: "{{ message }}"</p>
<p>Computed reversed message: "{{ reversedMessage }}"</p>
</div>
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#example',
data: {
message: 'Hello'
},
computed: {
// 计算属性的 getter
reversedMessage: function () {
// `this` 指向 vm 实例
return this.message.split('').reverse().join('')
}
}
})
计算属性缓存 vs 方法
<p>Reversed message: "{{ reversedMessage() }}"</p>
// 在组件中
methods: {
reversedMessage: function () {
return this.message.split('').reverse().join('')
}
}
我们可以将同一函数定义为一个方法而不是一个计算属性。两种方式的最终结果确实是完全相同的。然而,不同的是计算属性是基于它们的响应式依赖进行缓存的。只在相关响应式依赖发生改变时它们才会重新求值。这就意味着只要 message 还没有发生改变,多次访问 reversedMessage 计算属性会立即返回之前的计算结果,而不必再次执行函数。
这也同样意味着下面的计算属性将不再更新,因为 Date.now() 不是响应式依赖:
computed: {
now: function () {
return Date.now()
}
}
计算属性和侦听器的对比
<div id="demo">{{ fullName }}</div>
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
firstName: 'Foo',
lastName: 'Bar',
fullName: 'Foo Bar'
},
watch: {
firstName: function (val) {
this.fullName = val + ' ' + this.lastName
},
lastName: function (val) {
this.fullName = this.firstName + ' ' + val
}
}
})
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
firstName: 'Foo',
lastName: 'Bar'
},
computed: {
fullName: function () {
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName
}
}
})
- 计算属性的setter
// ...
computed: {
fullName: {
// getter
get: function () {
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName
},
// setter
set: function (newValue) {
var names = newValue.split(' ')
this.firstName = names[0]
this.lastName = names[names.length - 1]
}
}
}
// ...
- 侦听器
当需要在数据变化时执行异步或开销较侦听器watch
<div id="watch-example">
<p>
Ask a yes/no question:
<input v-model="question">
</p>
<p>{{ answer }}</p>
</div>
<!-- 因为 AJAX 库和通用工具的生态已经相当丰富,Vue 核心代码没有重复 -->
<!-- 提供这些功能以保持精简。这也可以让你自由选择自己更熟悉的工具。 -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios@0.12.0/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/lodash@4.13.1/lodash.min.js"></script>
<script>
var watchExampleVM = new Vue({
el: '#watch-example',
data: {
question: '',
answer: 'I cannot give you an answer until you ask a question!'
},
watch: {
// 如果 `question` 发生改变,这个函数就会运行
question: function (newQuestion, oldQuestion) {
this.answer = 'Waiting for you to stop typing...'
this.debouncedGetAnswer()
}
},
created: function () {
// `_.debounce` 是一个通过 Lodash 限制操作频率的函数。
// 在这个例子中,我们希望限制访问 yesno.wtf/api 的频率
// AJAX 请求直到用户输入完毕才会发出。想要了解更多关于
// `_.debounce` 函数 (及其近亲 `_.throttle`) 的知识,
// 请参考:https://lodash.com/docs#debounce
this.debouncedGetAnswer = _.debounce(this.getAnswer, 500)
},
methods: {
getAnswer: function () {
if (this.question.indexOf('?') === -1) {
this.answer = 'Questions usually contain a question mark. ;-)'
return
}
this.answer = 'Thinking...'
var vm = this
axios.get('https://yesno.wtf/api')
.then(function (response) {
vm.answer = _.capitalize(response.data.answer)
})
.catch(function (error) {
vm.answer = 'Error! Could not reach the API. ' + error
})
}
}
})
</script>
- Class 与 Style 绑定
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<script src="vue.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div
class="test"
v-bind:class="[ isActive ? 'active' : '', isGreen ? 'green' : '']"
style="width:200px; height:200px; text-align:center; line-height:200px;">
hi vue
</div>
<div
:style="{color:color, fontSize:size, background: isRed ? '#FF0000' : ''}">
hi vue
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vm = new Vue({
el : "#app",
data : {
isActive : true,
isGreen : true,
color : "#FFFFFF",
size : '50px',
isRed : true
}
});
</script>
<style>
.test{font-size:30px;}
.green{color:#00FF00;}
.active{background:#FF0000;}
</style>
</body>
</html>
<-! 如果isActive 的值为true 那么class 就是 active,如果为false 就是空;如果isGreen 的值为false 那么class就是green,如果为false 就是空--></-!>
v-bind:class="[ isActive ? 'active' : '', isGreen ? 'green' : '']"
<-! isRed 的值为true那么background 就是 #FF0000的颜色,如果是false 那么background 就是空--></-!>
:style="{color:color, fontSize:size, background: isRed ? '#FF0000' : ''}">
- 条件渲染
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<script src="vue.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div v-if="type === 'A'">
A
</div>
<div v-else-if="type === 'B'">
B
</div>
<div v-else-if="type === 'C'">
C
</div>
<div v-else>
Not A/B/C
</div>
<h1 v-show="ok">Hello!</h1>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vm = new Vue({
el : "#app",
data : {
type : "B",
ok : false
}
});
</script>
<style type="text/css">
</style>
</body>
</html>
<-! v-if 是真正意义的条件渲染,v-show 并不是,v-show 是会都渲染出来,只不过通过css样式,display 属性进行控制是否显示在页面></-!>
- 列表渲染
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<script src="vue.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="item,index in items" :key="index">
{{index}}{{ item.message }}
</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<li v-for="value, key in object" :key="key">
{{key}} : {{ value }}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vm = new Vue({
el : "#app",
data : {
items : [
{ message: 'Bar' },
{ message: 'I Fly'},
{ message: 'Foo' },
],
object: {
message: 'hello, vue.js!',
title: 'How to do lists in Vue',
author: 'Jane Doe',
publishedAt: '2016-04-10'
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
- 事件处理
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<script src="vue.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div id="example-1">
<button v-on:click="counter += 1"> 数值 : {{ counter }} </button><br />
<button v-on:dblclick="greet('abc', $event)">Greet</button>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vm = new Vue({
el : "#app",
data : {
counter: 0,
name : "vue"
},
methods:{
greet : function (str, e) {
alert(str);
console.log(e);
}
}
});
</script>
<style type="text/css">
</style>
</body>
</html>
Vue.js 为 v-on 提供了事件修饰符
<!-- 阻止单击事件继续传播 -->
<a v-on:click.stop="doThis"></a>
<!-- 提交事件不再重载页面 -->
<form v-on:submit.prevent="onSubmit"></form>
<!-- 修饰符可以串联 -->
<a v-on:click.stop.prevent="doThat"></a>
<!-- 只有修饰符 -->
<form v-on:submit.prevent></form>
<!-- 添加事件监听器时使用事件捕获模式 -->
<!-- 即内部元素触发的事件先在此处理,然后才交由内部元素进行处理 -->
<div v-on:click.capture="doThis">...</div>
<!-- 只当在 event.target 是当前元素自身时触发处理函数 -->
<!-- 即事件不是从内部元素触发的 -->
<div v-on:click.self="doThat">...</div>
- 表单输入绑定
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<script src="vue.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div id="example-1">
<input v-model="message" placeholder="edit me">
<p>Message is: {{ message }}</p>
<textarea v-model="message2" placeholder="add multiple lines"></textarea>
<p style="white-space: pre-line;">{{ message2 }}</p>
<br />
<div style="margin-top:20px;">
<input type="checkbox" id="jack" value="Jack" v-model="checkedNames">
<label for="jack">Jack</label>
<input type="checkbox" id="john" value="John" v-model="checkedNames">
<label for="john">John</label>
<input type="checkbox" id="mike" value="Mike" v-model="checkedNames">
<label for="mike">Mike</label>
<br>
<span>Checked names: {{ checkedNames }}</span>
</div>
<div style="margin-top:20px;">
<input type="radio" id="one" value="One" v-model="picked">
<label for="one">One</label>
<br>
<input type="radio" id="two" value="Two" v-model="picked">
<label for="two">Two</label>
<br>
<span>Picked: {{ picked }}</span>
</div>
<button type="button" @click="submit">提交</button>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vm = new Vue({
el : "#app",
data : {
message : "test",
message2 :"hi",
checkedNames : ['Jack', 'John'],
picked : "Two"
},
methods: {
submit : function () {
var submitObj = {
msg1 : this.message,
msg2 : this.message2,
chckname : this.checkedNames,
pck : this.picked
};
console.log(submitObj);
}
}
});
</script>
<style type="text/css">
</style>
</body>
</html>

